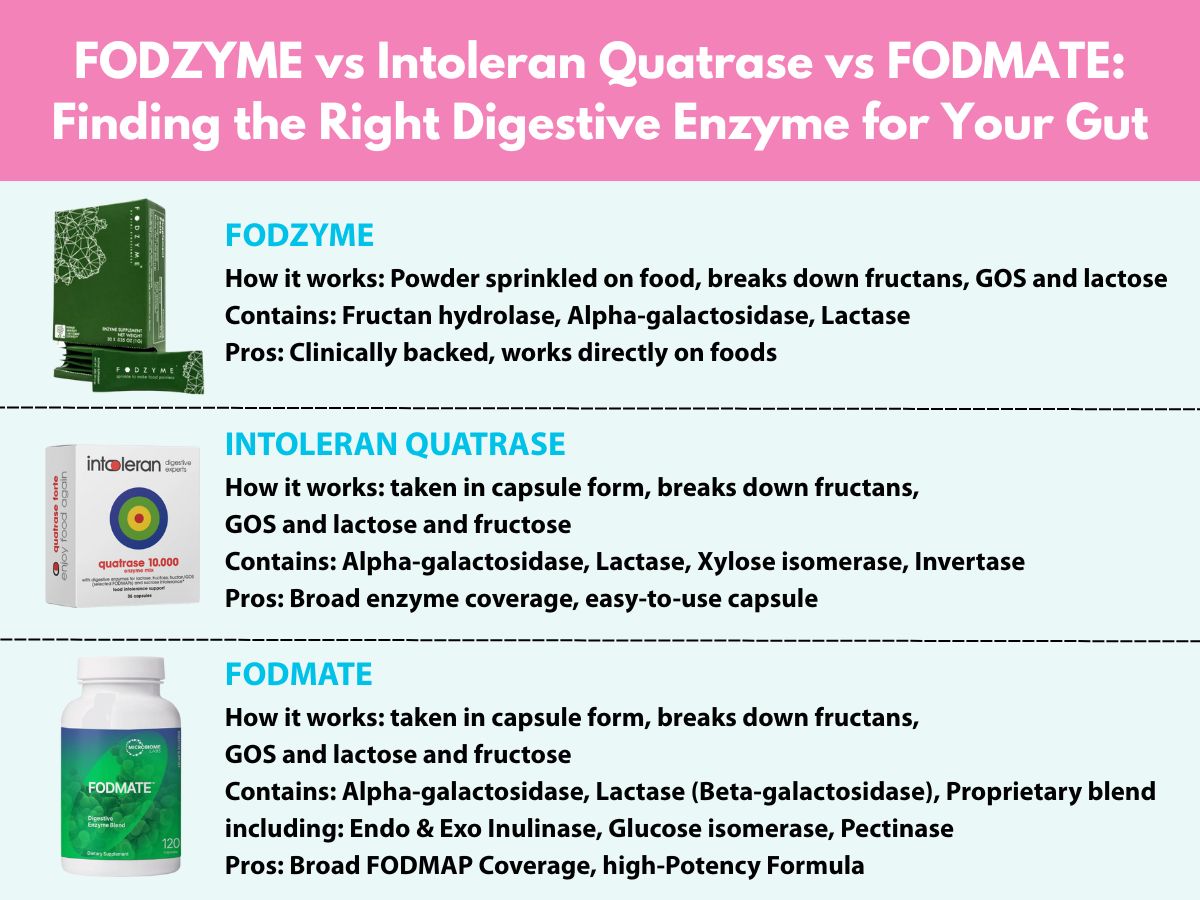
FODZYME vs Intoleran Quatrase vs FODMATE: Finding the Right Digestive Enzyme for Your Gut
If you are following a low FODMAP diet or managing symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), digestive enzyme supplements may offer some relief — especially if certain carbohydrates are hard for you to digest. While these enzymes aren’t a cure for IBS, they can help improve tolerance to trigger foods like garlic, onion, dairy, legumes, and certain fruits.
In this guide, we break down three popular enzyme products — FODZYME, Intoleran Quatrase, and FODMATE™ — and compare how they work, what they target, and who they may suit best.
What Do Digestive Enzymes Do?
Digestive enzymes help break down complex carbs — particularly FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols) — that often trigger symptoms in IBS sufferers. These carbs can draw water into the gut and ferment quickly in the large intestine, causing bloating, gas, and discomfort.
By supplementing with targeted enzymes, you may be able to digest some of these FODMAPs before they cause problems.
1. FODZYME
How it works:
FODZYME uses a blend of enzymes to break down common FODMAPs like fructans (in garlic and onion), GOS (in legumes), and lactose (in dairy) before they reach the large intestine. You sprinkle the powder directly onto your food, and it starts working in your stomach during digestion.
Contains:
- - Fructan hydrolase – for fructans
- - Alpha-galactosidase – for GOS
- - Lactase – for lactose
Clinical Insight:
Studies showed that FODZYME can break down up to 90% of a 3g fructan dose — the equivalent of about six garlic cloves! [1]
Pros:
- -Clinically backed
- -Works directly on food
- -Vegan, gluten-free, and Monash University Low FODMAP Certified
- -Great for eating out or takeaway
Cons:
- -Doesn’t target polyols (sorbitol, mannitol) or excess fructose
2. Intoleran Quatrase
How it works:
Quatrase helps break down a wider range of FODMAPs, including fructose and sucrose, in addition to GOS and lactose. It’s taken in capsule form about 10 minutes before a meal.
Contains:
- -Alpha-galactosidase – for GOS
- -Lactase – for lactose
- -Xylose isomerase – converts fructose to glucose
- -Invertase – for sucrose
Pros:
- -Broad enzyme coverage
- -Easy-to-use capsule
- -Monash University Low FODMAP Certified
Cons:
- -Not as fast-acting as food-applied enzymes
- -Doesn’t cover polyols
3. FODMATE™ by Microbiome Labs
How it works:
FODMATE is designed to provide short-term support when eating high-FODMAP meals. It contains a wide range of enzymes that break down multiple types of carbohydrates — from fructans and pectin to lactose and fructose. However, it’s not recommended for daily or long-term use.
Contains:
- -Alpha-galactosidase – in a higher amount than most competitive formulas
- -Lactase (Beta-galactosidase) – in a higher amount than most competitive formulas
-
-Proprietary blend including:
- Endo & Exo Inulinase – for inulin/fructans
- Glucose isomerase – for fructose
- Pectinase – for fermentable pectin
Pros:
- -Comprehensive FODMAP coverage (except polyols)
- -Helps ease symptoms when eating out or during diet transitions
- -Supports diet compliance and flexibility
Cons:
- -Cannot be sprinkled on food
- -Does not cover polyols
Final Thoughts:
- -FODZYME is perfect for on-the-go use or dining out, especially when meals may contain hidden garlic or onion. Its powder format makes it easy to sprinkle directly on food for immediate action.
- -Intoleran Quatrase is a reliable capsule option if you are intolerant to multiple sugars, including fructose, GOS, and lactose. It is convenient for everyday use and supports broader digestive needs.
- -FODMATE™ is the most budget-friendly option, priced under $100 for 120 capsules. It offers comprehensive coverage for many FODMAP groups — though not polyols — and is best suited for short-term or occasional support.
As always, speak with your dietitian or healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you're managing IBS or other gastrointestinal conditions.
References:
[1] Ochoa KC, Samant S, Liu A, Duysburgh C, Marzorati M, Singh P, Hachuel D, Chey WD, Wallach T. In vitro efficacy of targeted fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols enzymatic digestion in a high-fidelity simulated gastrointestinal environment. Cell Reports Medicine. 2022;3(12):100846. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100846
2 comments
-
Biggest problem is onions and garlic. Which product will be the best choice. Tired of sushi restaurants as my only option.
Rob
Janet: Only Fodmate and Fodzyme will work on onion/garlic. Both are equally effective, with Fodmate being about 1/2 the price of Fodzyme.